字母异位词分组#
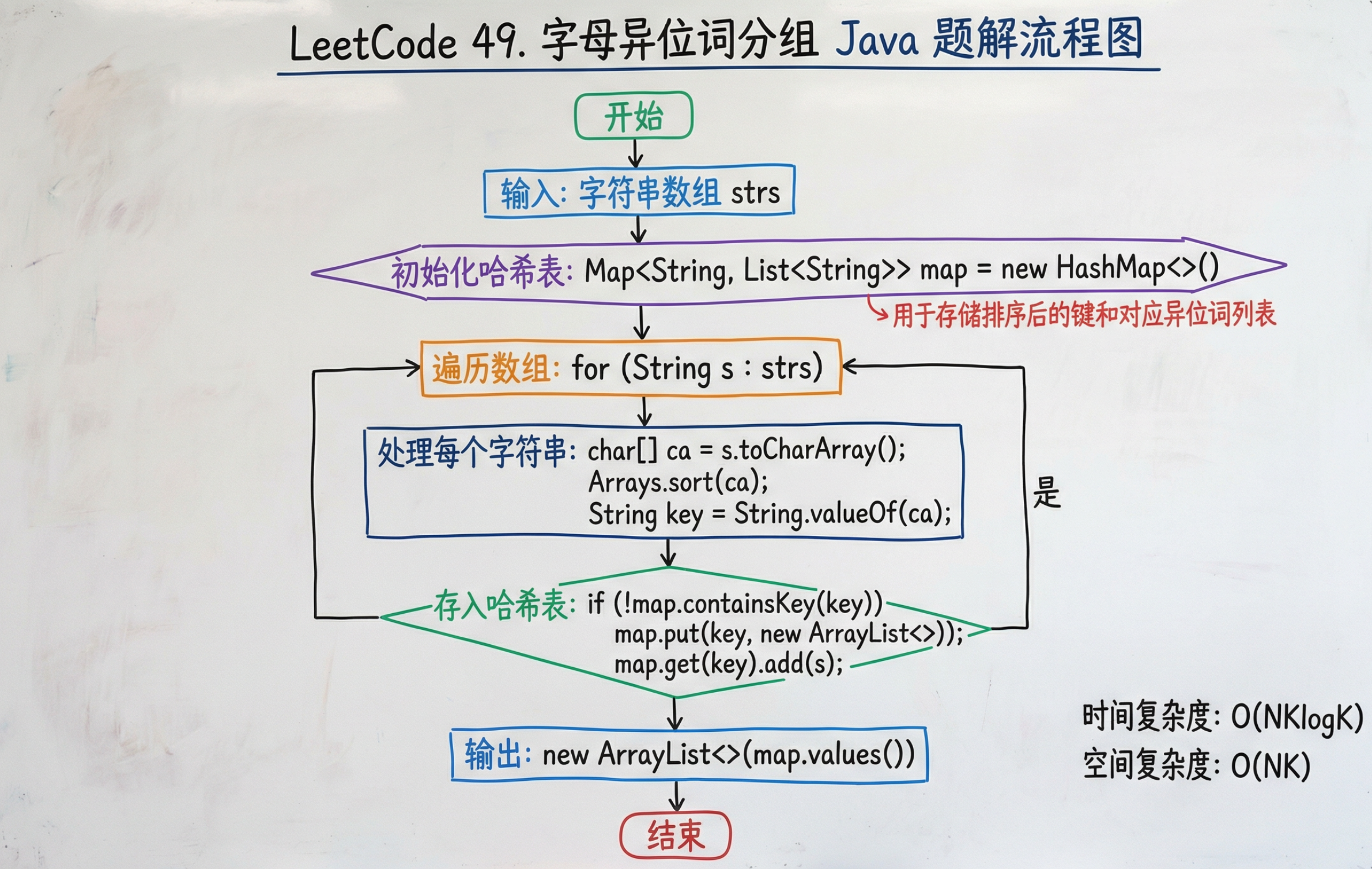
解法 1:先排序,再 hash#
优点:简单,易于实施。
使用 lambda 表达式解题:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
return Arrays.stream(strs)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> {
char [] ch = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ch);
return new String(ch);
}))
.values()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
|
更加简化写法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ch);
map.computeIfAbsent(String.valueOf(ch), k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
|
当 Map 里没有某个 key 时,就用你传入的 lambda 生成一个默认值放进去,并返回这个值;如果 key 已存在,就直接返回已有值。它非常适合“分组/聚合”这类场景。
Go 语言写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| func groupAnagrams(strs []string) [][]string {
m := make(map[string][]string, len(strs))
for _, s := range strs {
b := []byte(s)
sort.Slice(b, func(i, j int) bool {return b[i] < b[j]})
key := string(b)
m[key] = append(m[key], s)
}
res := make([][]string, 0, len(m))
for _, v := range m {
res = append(res, v)
}
return res
}
|
Python 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class Solution:
def groupAnagrams(self, strs: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
mp = defaultdict(list)
for s in strs:
key = ''.join(sorted(s)) # 通用:排序作为 key
mp[key].append(s)
return list(mp.values())
|
- defaultdict 会创建一个默认的 dict,在访问某个 value 不存在的 key 时,会自动调用传入的工厂函数来设置 value 值。
JS 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| /**
* LeetCode 49 - Group Anagrams
* 通用写法:排序后字符串作为 key
* 时间复杂度:O(n * k log k)(k 为单词平均长度)
* 空间复杂度:O(n * k)
*
* @param {string[]} strs
* @return {string[][]}
*/
function groupAnagrams(strs) {
const map = new Map(); // key -> string[]
for (const s of strs) {
const key = s.split("").sort().join(""); // 规范化 key
if (!map.has(key)) map.set(key, []);
map.get(key).push(s);
}
return Array.from(map.values());
}
|
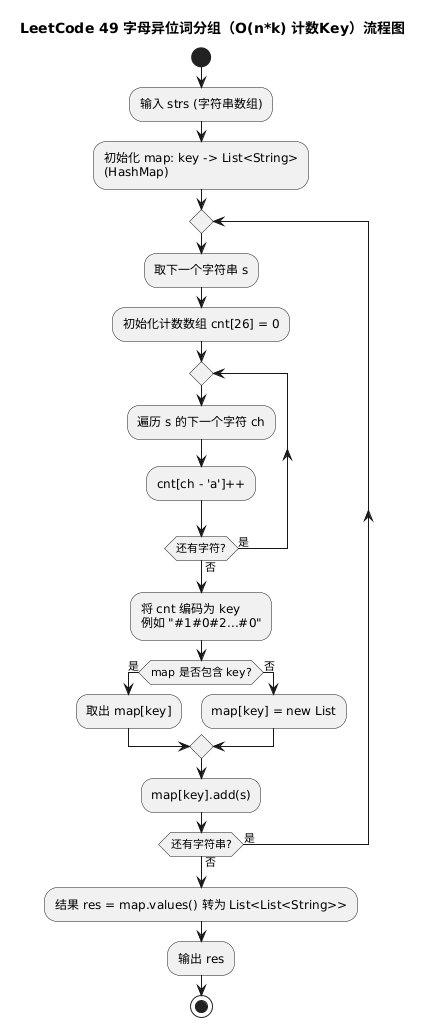
O(n*k) 复杂度写法#
Java 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(strs.length * 2);
for (String s : strs) {
int[] cnt = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
cnt[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
// 用计数向量编码成 key:#1#0#0...(避免歧义)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(26 * 2);
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
sb.append('#').append(cnt[i]);
}
String key = sb.toString();
map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
|
更加简洁的写法是,可以直接生成 array 的 hashcode,虽然有概率哈希冲突。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<Integer, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(strs.length * 2);
for (String s : strs) {
int[] cnt = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
cnt[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
Integer key = Arrays.hashCode(cnt);
map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
|
同时,我们甚至能直接使用 list 作为 key:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<List<Integer>, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(strs.length * 2);
for (String s : strs) {
Integer[] cnt = new Integer[26];
Arrays.fill(cnt, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
cnt[s.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
map.computeIfAbsent(new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(cnt)), k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(s);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
|
Go 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| func groupAnagrams(strs []string) [][]string {
mp := make(map[[26]byte][]string)
for _, s := range strs {
var key [26]byte
for i := 0; i < len(s); i ++ {
key[s[i] - 'a'] ++
}
mp[key] = append(mp[key], s)
}
res := make([][]string, 0)
for _, v := range mp {
res = append(res, v)
}
return res
}
|
Go 语言还可以这么写:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| func groupAnagrams(strs []string) [][]string {
mp := make(map[string][]string)
for _, s := range strs {
var key [26]byte
for i := 0; i < len(s); i ++ {
key[s[i] - 'a'] ++
}
keyStr := string(key)
mp[keyStr] = append(mp[keyStr], s)
}
res := make([][]string, 0)
for _, v := range mp {
res = append(res, v)
}
return res
}
|
Python 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution:
def groupAnagrams(self, strs: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
mp = defaultdict(list)
for s in strs:
cnt = [0] * 26
for ch in s:
cnt[ord(ch) - ord('a')] += 1
mp[tuple(cnt)].append(s) # O(1) 哈希 key(按 26 维计数)
return list(mp.values())
|
python 写法中需要注意的是,字符转整数需要通过 ord 转,不能直接进行计算。
tuple 可以作为 map 的 key,其他不行。
JS 写法#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| function groupAnagrams(strs) {
const map = new Map(); // key -> string[]
for (const s of strs) {
const cnt = new Array(26).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
cnt[s.charCodeAt(i) - 97]++; // 'a' 的 ASCII/Unicode 码点是 97
}
// 计数数组转 key(加分隔符避免歧义)
const key = cnt.join("#");
if (!map.has(key)) map.set(key, []);
map.get(key).push(s);
}
return Array.from(map.values());
}
|
需要注意的是,js 中,charAt 返回的是字符串,而 charCodeAt 才返回整数。